
ArrayLists are not type-safe, and therefore must be boxed, and unboxed otherwise an error at runtime will occur. Unfortunately ArrayLists are inefficient compared to arrays and Generic Lists. It can store many types of variable except for a multi-dimensional array. There are both advantages and disadvantages to ArrayLists.Īn ArrayList is a flexible list of objects that can be dynamically resized and accessed through Integer indexing. This means two different classes like string and integer can be stored together in a single collection. ArrayLists are a type of collection that can be used to store various types of data.
They are implemented in many programming languages such as Java, C# and C++. They were implemented to be more flexible collections than arrays. Thanks for reading.ArrayLists have been used by programmers since the late 90’s. Insertion and deletion is slow with ArrayList because, during these operations ArrayList need to adjust the indexes according to deletion or insertion if we are performing on middle indexes. So in LinkedList access is slow because for accessing elements we need to navigate through the elements one by one.īut insertion and deletion is much faster with LinkedList, because if we know the node, just need to change the pointer before or after the node where we want to insert or which one we want to delete. But accessing elements in LinkedList are difficult.

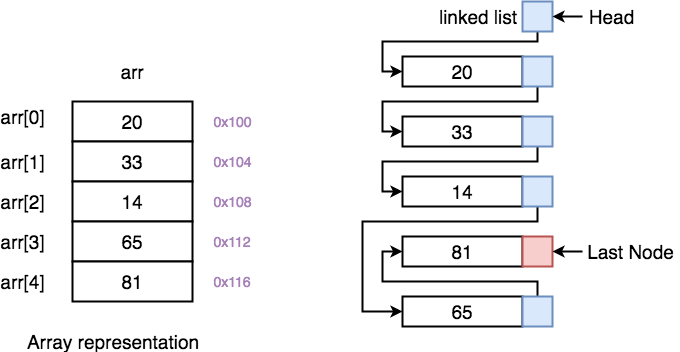
SummaryĪccessing elements are faster with ArrayList, because it is index based. LinkedList has more memory overhead than ArrayList because in ArrayList each index only holds actual object (data) but in case of LinkedList each node holds both data and address of next and previous node.
by calling remove(index), ArrayList performs at the rate of O(n) while LinkedList needs to traverse to that point which also makes it O(n/2), as it can traverse from either direction based upon proximity. In order to remove an element from a particular index e.g. Adding elements in ArrayList is O(1) operation if it does not trigger the re-size of the Array.
#Linked list using array vs arraylist update#
ArrayList also needs to update its index if we insert new element anywhere except at the end of ArrayList.
#Linked list using array vs arraylist full#
Insertions are easy and fast in LinkedList as compared to ArrayList because there is no risk of resizing the array and copying content to new array if array gets full which makes adding into ArrayList of O(n) in worst case, while adding is O(1) operation in LinkedList in Java as it does not require any navigation. LinkedList is also implemented as doubly linked list and for index based operation navigation can happen from either end. On the Other hand LinkedList does not provide random or index based access and we need to iterate over linked list to retrieve any element which is of order O(n).Īpart from the List interface, LinkedList also implements Dequeue interface, which provides first in first out (FIFO) operations and several other Dequeue functions. ArrayList provides O(1) performance for get(index) method but remove is costly in ArrayList as we need to rearrange all elements. Getting elements from ArrayList with index is pretty fast. DifferencesĪrrayList is backed by Array while LinkedList is backed by LinkedList. It means they will throw ConcurrentModificationException if collection is modified structurally once Iterator is created. Iterator of both LinkedList and ArrayList are fail-fast. So they maintain insertion order of elements, i.e., first element will be added on first position.ĪrrayList and LinkedList also allow duplicates and null value.

Therefore we can pass either ArrayList or LinkedList if a method accepts List interface.īoth ArrayList and LinkedList are not synchronized, it means we cannot share them among multiple threads in a concurrent environment without external synchronization.ĪrrayList and LinkedList both are ordered collection. Similaritiesīoth ArrayList and LinkedList are implementations of List interface. In this tutorial we will discuss what are the similarities and differences found between ArrayList and LinkedList. ArrayList and LinkedList are two popular concrete implementations of List interface from Java’s popular Collection framework.īeing List implementations both ArrayList and LinkedList are ordered, index based and allows duplicate.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
